When mortar fails, projects face costly delays. Cracks, weak bonding, or poor workability often come from choosing the wrong additive. The right choice ensures long-term reliability and consistent performance.
RDP improves adhesion, flexibility, and water resistance, while HPMC enhances water retention, workability, and sag resistance. Together, they form the backbone of modern mortar systems, making projects stronger and easier to apply.
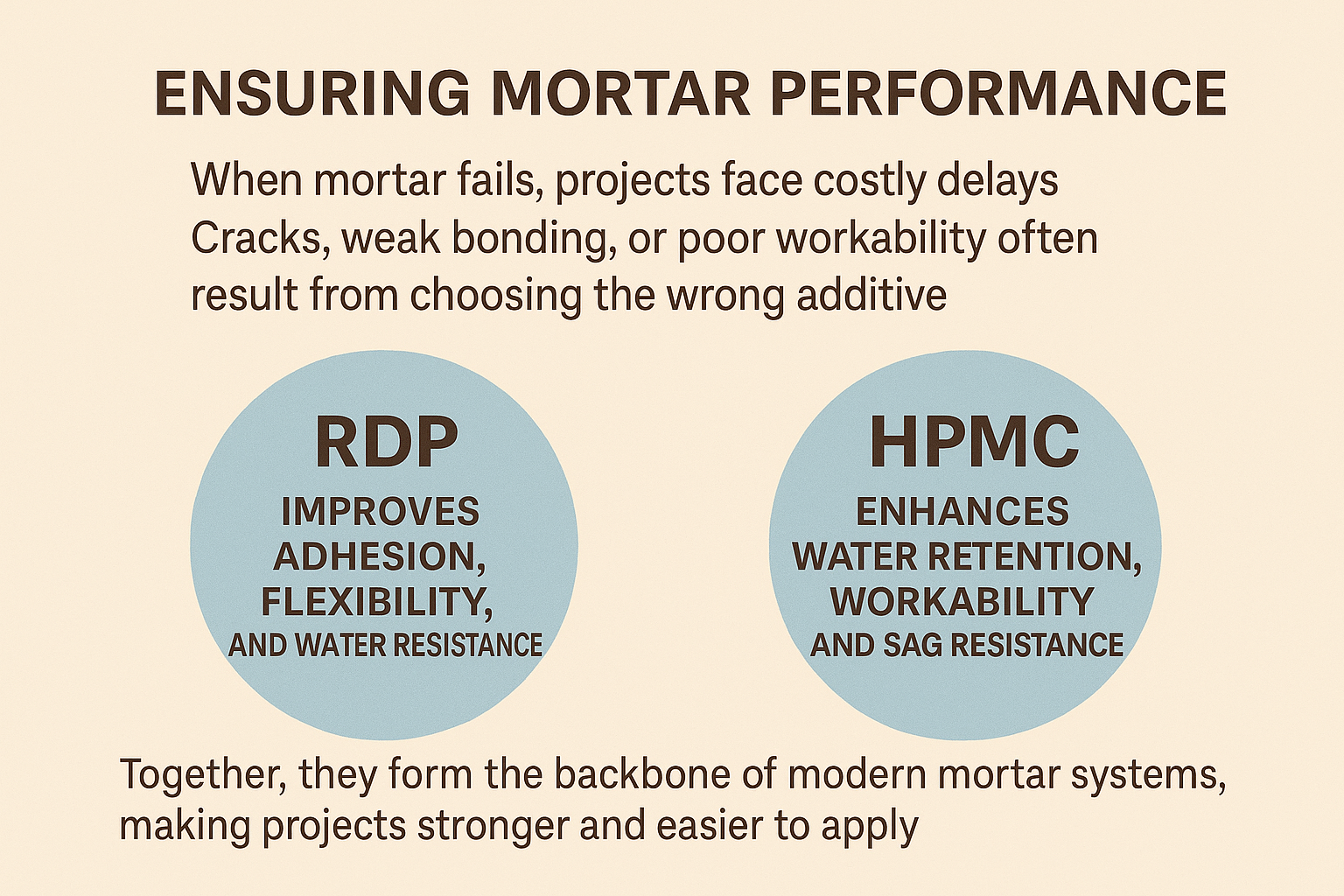
RDP vs HPMC in mortar
Mortar design today is more complex than ever. Procurement managers and formulation engineers must consider not only cost but also performance and reliability. By understanding how RDP and HPMC function, and how they complement each other, you can make smarter choices for projects of all scales.
What Roles Do RDP and HPMC Play in Mortar Formulations?
Problems like poor adhesion, cracks, or mortar shrinkage are common when additives are missing. Many buyers focus only on cost and overlook what functions these key additives actually provide.
RDP gives mortar strong bonding strength, flexibility, and water resistance, while HPMC provides water retention, workability, and sag resistance. Each plays a different but critical role in achieving reliable mortar performance.
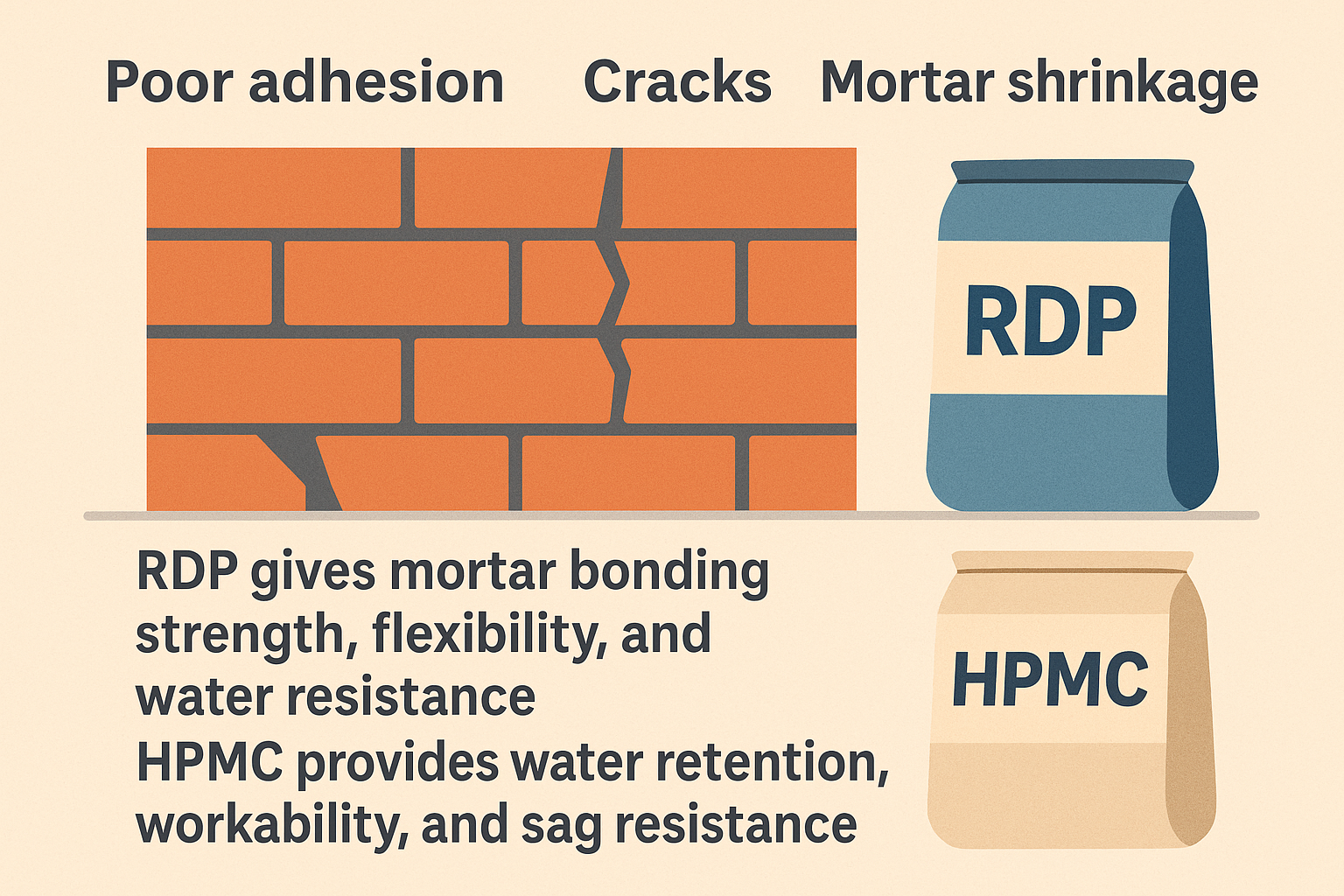
Roles of RDP and HPMC in mortar
RDP is a polymer powder that redisperses in water to form a stable emulsion. Its main function is to improve adhesion between cementitious materials and substrates. In addition, it provides flexibility that helps mortars resist cracking under stress. Because of its film-forming ability, RDP also increases water resistance, which is critical in exterior applications and wet areas.
On the other hand, HPMC is a cellulose ether that dissolves in water and works as a thickener. Its main role is to hold water inside the mortar, preventing premature drying. This ensures proper hydration of cement, leading to better strength development. It also improves workability by making the mortar easier to spread and reducing sagging on vertical surfaces.
Here is a structured comparison:
| Additive | Main Function | Benefits in Mortar |
|---|---|---|
| RDP | Adhesion & flexibility | Strong bonding, crack resistance, water resistance |
| HPMC | Water retention & rheology control | Better workability, reduced sagging, longer open time |
Together, they cover both structural and application needs, making mortar formulations more reliable.
How Do RDP and HPMC Complement Each Other in Tile Adhesives and EIFS?
Tile adhesives often fail when they lack flexibility or dry too fast. EIFS systems can also crack if water retention or bonding strength is poor. These issues happen when only one additive is considered.
RDP and HPMC complement each other instead of replacing each other. RDP provides bonding and flexibility, while HPMC controls water retention and workability. Their synergy makes adhesives and EIFS systems both durable and easy to use.

RDP and HPMC in tile adhesives and EIFS
In tile adhesives, HPMC ensures that water remains long enough for cement hydration, preventing tiles from losing adhesion due to rapid drying. RDP adds bonding strength, ensuring tiles stay firmly attached even under heavy use. The flexibility of RDP also prevents cracks from stress or temperature changes. When used together, adhesives become more reliable both during installation and in long-term use.
In EIFS (External Insulation and Finish Systems), the synergy is even more important. These systems must deal with thermal expansion, moisture, and wind pressure. HPMC controls consistency during application and avoids sagging on vertical walls. RDP ensures the mortar adheres strongly to insulation boards and provides elasticity to withstand structural movement.
Key synergy points
| Application | Role of HPMC | Role of RDP | Combined Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tile Adhesive | Water retention, anti-sag | Adhesion, flexibility | Easy to apply and long-lasting bond |
| EIFS | Workability, crack resistance | Elasticity, durability | Strong, flexible insulation systems |
This complementary effect is why most professional formulations for adhesives and EIFS always combine both additives. Engineers and procurement managers should not view them as alternatives but as partners in performance.
Which Factors Should You Consider When Choosing Between RDP and HPMC?
Many buyers face confusion: should they choose RDP or HPMC? Some focus only on cost, while others look at technical features without thinking of the application. Both approaches often lead to poor results.
The right choice depends on the application, performance requirements, and cost considerations. Procurement managers and formulation engineers should match each additive to project needs instead of replacing one with the other.

Factors when choosing RDP and HPMC
When choosing between RDP and HPMC, application type is the first factor. For tile adhesives that require strong bonding, both additives are necessary. HPMC ensures water retention and application ease, while RDP provides adhesion and flexibility. For plastering or putty, HPMC alone can sometimes be enough, especially when the main goal is water retention and smooth application. However, in exterior systems like EIFS, both are mandatory to guarantee long-term durability.
Performance requirements also guide decisions. If the project needs high crack resistance, RDP is critical. If it requires long open time and smooth spreading, HPMC is key. In some cases, adjusting the dosage of each can achieve a balance between cost and performance.
Cost is the final consideration. HPMC and RDP differ in price, and buyers often try to cut costs by using less. But skipping one of them may cause failures that cost much more in rework. A balanced formulation, supported by supplier guidance, offers the best long-term value.
For further technical references, standards like EN 12004 for tile adhesives and EIFS guidelines from EIMA provide benchmarks for performance requirements. By aligning choices with these standards, decision-makers can avoid common risks and ensure compliance.
Conclusion
RDP and HPMC are not competitors but partners. Each plays a unique role, and together they provide bonding, flexibility, water retention, and workability that make mortar systems reliable and efficient.



